This collision resulted in furrows on the surface of Ganymede.
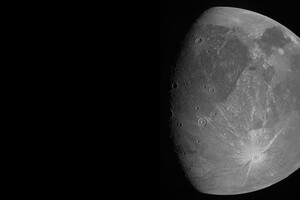
Depressions that can be seen on most of the surface the largest satellite in the solar system, Ganymede, probably appeared as a result of a collision with a celestial body with a diameter of about 150 kilometers. These are the conclusions reached by Japanese scientists, according to Forbes.
Ganymede is the largest of Jupiter's 79 moons. It is larger than Pluto and Mercury, its diameter is 5268 kilometers. It is the only known satellite of the planet with its own magnetic field. Ganymede also has an atmosphere and is believed to be a salty ocean beneath the surface.
Read also: Juno Station recorded the sound of one of Jupiter's moons
Ganymede's surface is speckled, grooved, and patterned. In the article, scientists claim that these furrows are part of a concentric system of tectonic deflections.
“If this multi-ring structure has a shock origin, it is the largest shock structure known in the solar system. It is difficult to estimate the size of the fallen object, but the diameter of the furrows is consistent with the diameter of about 150 kilometers, “- said the scientists.
“, As well as the Galileo spacecraft, which was in the orbit of Jupiter's moon in 2001-2003. Ganymede was also photographed by Juno Station in June 2021.
The scientists' theory can be confirmed by observations made by the European Space Agency's JUICE (Jupiter Icy moon Explorer) mission. It is scheduled to launch on April 5-25, 2023, it will arrive in the Jupiter system in 2031 and spend 3.5 years studying the gas giant and its satellites Callisto and Europe. In 2032, the station will move into Ganymede's orbit and will be the first spacecraft to orbit the planet's satellite, other than those studying the moon. Researchers have found evidence for the hypothesis that moist convection – when hot and less dense air rises – is the driving force behind these cyclones.




